Introduction
As the world’s largest producer and exporter of kieserite, China's market output is a key barometer for global trade stability and price trends. In the first half of 2025, despite macroeconomic uncertainties and regional input disruptions, global demand across agriculture, horticulture, water treatment, and industrial segments remained resilient. This review, rooted in China Customs data and port-level statistics, explores export volume trends, domestic price fluctuations, and regional trade flow across Asia, South America, Europe, and North America. It culminates in quantitative forecasts for demand and price growth in H2 2025 and 2026.
1. China’s Export Leadership and Comparative Price Trends
China solidified its role as the leading global exporter of kieserite in H1 2025, supplying 56% of total global shipments. According to China Customs (Jan–May 2025), Q1 2025 export volume reached 298,000 MT, marking a 22.1% year-on-year increase—from approximately 244,000 MT in Q1 2024 to 298,000 MT in Q1 2025.
This leadership rests on:
(a) Integrated Supply Chain & Regional Scale
Production clusters in Liaoning, Shandong, Tianjin, and Qingdao are strategically located near major magnesite reserves in northeastern China. This proximity allows for raw material sourcing within a 200–300 km radius, reducing inland transport costs by an estimated 15–20% compared to European producers, who often rely on rail and road shipment to ports such as Hamburg and Rotterdam.
These industrial hubs benefit from large-scale, modernised facilities, particularly in Haicheng, Dashiqiao, and Weifang, where automated production lines have enabled annual kieserite output exceeding 400,000 MT. The resulting production scale not only supports tight batch-to-batch nutrient consistency but also allows for timely fulfilment of bulk agricultural demand cycles in Southeast Asia, South America, and Europe.
(b) Export Cost Efficiency and Port-Side Logistics
Chinese kieserite maintains a 10–15% FOB price advantage over key competitors—Brazil and Germany—not only due to lower production costs but also due to superior port accessibility and container throughput capacity. Ports like Qingdao and Dalian offer direct deep-sea routes and lower drayage costs, enabling more flexible scheduling for containerised shipments or break-bulk exports depending on end-market structure.
(c) Performance and Quality Consistency
Beyond logistics, Chinese kieserite exhibits formulation consistency that appeals to international buyers with high agronomic standards. Typically containing 25–27% MgO and low chloride levels (<0.1%), it is suitable for chloride-sensitive crops such as citrus, grape, and mango. This purity enables more precise nutrient application and safer use in high-value cropping systems.
In comparison:
German kieserite, priced at a 12–15% premium, offers similar MgO levels but shows greater batch variability in granule size and dissolution rate. These inconsistencies may complicate fertigation and mechanised broadcast systems. Inland plant locations also lack deep-water port access, adding an estimated 12–15% to inland freight costs.
Brazilian kieserite, priced 8–10% higher, is often sourced from Minas Gerais and Goiás—inland production zones requiring road–rail–port chains that add $20–25/MT in transport. It also tends to exhibit higher chloride impurity levels (0.4–0.6%), which limits suitability for horticultural applications and export crops subject to strict residue standards.
2. H1 2025 Price Volatility: Anatomy of a Supply Shock
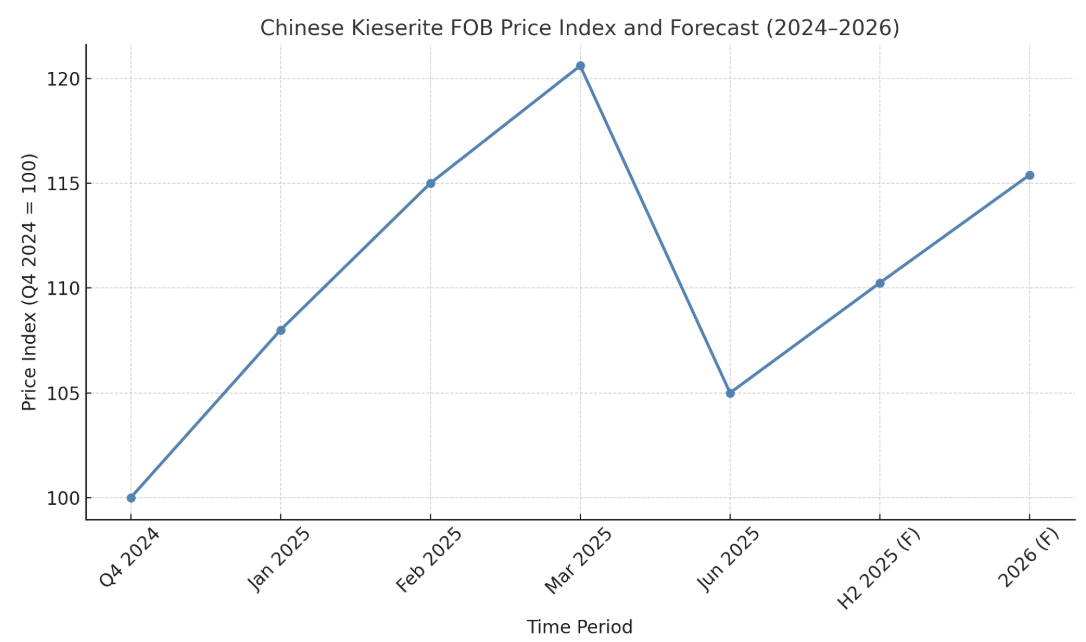
China's internal price index for kieserite rose by 20.6% QoQ by March 2025, reflecting a sharp, synchronised response to three primary supply disruptions:
In Q4 2024 and early 2025, sulphuric acid—a critical input for kieserite production—experienced substantial supply disruptions across China, driving significant price escalation.
Two key regional events contributed to this shortage:
As a net result of these concurrent disruptions, sulphuric acid prices rose by 35% year-on-year in early Q1 2025, per data from the China Sulphuric Acid Association. This price surge directly increased production costs for kieserite, particularly affecting 60% of northern Chinese producers dependent on Shanxi and Inner Mongolian supply chains.
These upstream shocks laid the foundation for the sharp quarter-on-quarter FOB price escalation of kieserite seen in Q1 2025.
Logistical Bottlenecks
Qingdao Port, normally handling 90,000 MT/month of general bulk, saw capacity drop by nearly 30% due to vessel scheduling conflicts and temporary rail disruption. Stock dropped to 18,000 MT, its lowest in three years (the previous 5-year average was 28,000–32,000 MT). As buyers faced shortages, domestic prices increased sharply.
Policy & Safety Interruptions
In mid-April 2025, a serious explosion at the Haicheng Huayu Chemical Plant, located in Panjin City, Liaoning Province, triggered immediate regulatory intervention. The incident—confirmed to have occurred on April 12, 2025—resulted in multiple injuries and widespread operational hazards, prompting the Liaoning Provincial Emergency Management Department to initiate a 48-day province-wide safety inspection covering 25 chemical and mineral processing facilities.
During the review period, kieserite production in Liaoning—the largest producing province in China—was significantly curtailed. Government dispatches indicated an average weekly output loss of 9,200 MT, equivalent to approximately 18% of total provincial kieserite capacity. The restrictions affected both active calcination and magnesium sulphate synthesis units in Anshan, Yingkou, and Panjin districts.
This temporary production cutback exacerbated supply constraints already stressed by feedstock shortages in Shanxi and Inner Mongolia. Though operations began to gradually resume by late May, the four-week output gap coincided with peak seasonal demand preparations in Southeast Asia and Latin America, further tightening spot availability and contributing to upward FOB price movement.
By June, feedstock replenishment, restored port operations, and resumed northeast production lowered the domestic index by 12–13% QoQ. The correction reflected decreased scarcity and restored logistics, linking supply normalisation with pricing ease.
3. H2 2025 Outlook: Feedstock Market Rebalancing
Forecast models indicate a 5–8% price rise in H2 2025. Government data show sulphuric acid output in Shandong increased by 15% MoM by May–June 2025. Additionally, magnesium carbonate prices moderated by ~8% from March peaks, stabilising input costs. Nevertheless, post-shock regulatory compliance (energy and emissions certificates) absorbs 40–50% of cost relief, softening price relief for downstream products.
4. 2026 Forecast: Energy Policy Effects
An overall price rise of 4–6% is expected in 2026, driven by structural constraints and evolving demand. Under China’s "dual control" (carbon and energy intensity limits), Liaoning Development and Reform Commission projections indicate output curtailment of up to 25% at mid-tier Kieserite plants in early 2026. Reduced output volume could accentuate global scarcity, lifting prices moderately.
5. Export Data Insights from China Customs
Conclusion
China remains the dominant supplier in the global Kieserite market, accounting for over half of global exports during H1 2025. Although a 20.6% price spike occurred due to raw material and logistical constraints, normalising trends led to a 12–13% correction by June. Moving into H2 2025, prices are projected to grow 5–8%, buoyed by seasonal demand and emerging policy costs, with a further 4–6% increase expected in 2026 owing to planned energy restrictions and steady agricultural consumption. Supported by China Customs data and macroeconomic indicators, this forecast positions China as both a volume anchor and pricing benchmark in the international Kieserite arena.
If you have any questions, please fill in the relevant information. We are very willing to provide more information and a full range of services for both you and your company.