Introduction
This analysis examines 2025 mid-year and forward demand dynamics for Chinese kieserite—magnesium sulphate monohydrate across Asia, South America, Africa, Europe, and North America. Drawing on Chinese Customs data and partner-country import statistics, it explores whether demand in key markets is likely to increase or decline in H2 2025, the underlying causes, and whether any such volume shifts are likely to introduce notable price volatility. Finally, it presents demand forecasts for 2026, supported by macroeconomic drivers.
Demand Trends in Key Markets
1. Asia
1.1 Malaysia
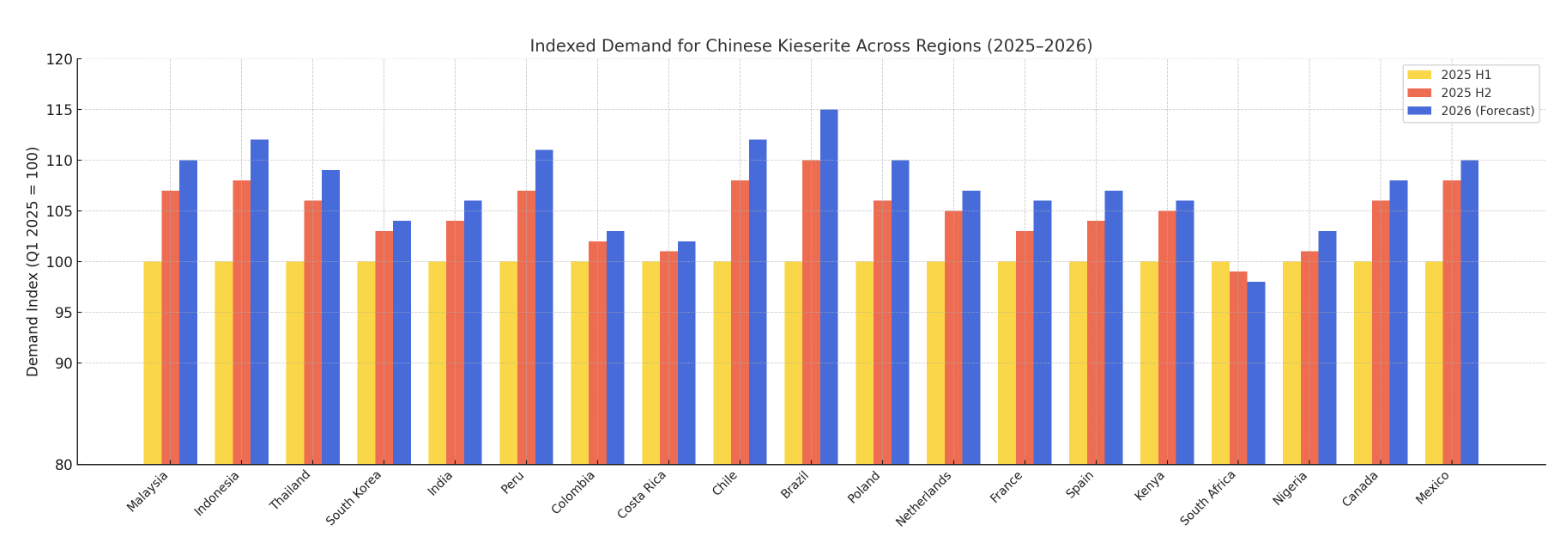
In Q1 2025, Malaysia’s imports of kieserite rose ≈7.5% year‑on‑year, supported by government-fertiliser subsidy programmes targeting palm and rubber plantations. Official statements from Malaysia's Ministry of Agriculture cite increasing magnesium uptake for enhancing chlorophyll synthesis and yield in oil palm estates and smallholder rubber farms. These crops typically respond to granular kieserite applications of 25–35 kg/ha. With continued subsidy coverage and agro-extension campaigns, demand in H2 2025 is expected to increase by roughly 5–7% over H1. Given strong demand underlying incremental volumes, market pricing is expected to remain stable, with only limited upward pressure of 2–3%, reflecting enhanced volume and steady supply.
1.2 Indonesia
Indonesia imported approximately 106,000 tonnes of kieserite in 2024. Customs and trade data show import volume rose ~8% YoY in H1 2025, largely attributable to expanded use in oil palm cultivation: plantations are increasingly using magnesium-enriched fertilisers to boost FFB weight, oil content, and crop resilience, particularly in Riau and Kalimantan regions. Assuming acreage growth of 4–5% in late 2025, demand is projected to rise further by 6–8% in H2 2025. This growth could generate mild upward pressure on price, possibly 3–5%, due to seasonal replenishment before dry season preparations. Provided Chinese export logistics remain efficient, major disruptions are unlikely.
1.3 Thailand
Thailand’s January–May 2025 imports increased 6.8% YoY, with the 2024 total volume around 48,000 tonnes. Demand derives from both horticulture (orchards, flowers) and livestock feed additives, especially in the Northeast rice belt and poultry sector. With fruit export targets rising and livestock feed demand steady, H2 2025 demand is poised to increase by ~5–6%. Because buyers in smaller batches (e.g. packaging sizes) dominate, demand-driven price movements are expected to be mild, likely a 2–3% rise, reflecting steady contracting and inventory restocking.
1.4 South Korea
Imports remained largely stable in Q2 2025, with uptake for greenhouse agriculture (e.g. tomatoes, peppers) and potable water treatment plants. Korean industry reports indicate domestic greenhouse usage of kieserite grew approximately 3% in early 2025, tied to Revised Agricultural Standards for hydroponic clarity and EU food safety export alignment. Water treatment plants in metropolitan areas like Seoul and Busan are deploying kieserite as a flocculant for sulphate removal, adding 2–3% incremental usage volume. Consequently, South Korean kieserite demand is expected to increase slightly by 2–4% in H2. Price impact should be minimal, with a possible <2% increase due to long-term contracts and small incremental volumes.
1.5 India
According to recent India market reports, the India magnesium sulphate market is forecast to grow at a ~2–3% annual rate over 2025–2029. Domestic use is focused on agriculture—particularly rice, cotton, and mangoes—where magnesium deficiency is common in monsoonal soils. Public procurement statistics and trade commentary suggest India started importing Chinese kieserite in volumes exceeding 50,000 tonnes/year in 2024, rising ~4% in H1 2025. Demand is steady due to the government fertiliser subsidy continuation and increasing awareness among farmers of nutrient-balanced fertilisation. H2 2025 is expected to record a small increase of ~4%, and assuming input costs remain constrained, price implications are limited—perhaps a 2% upward tick reflecting logistic seasonality.
2. South America
2.1 Peru
Callao Port data show a 9% rise in kieserite imports during Q1 2025, closely matching an 8% expansion in coffee and sugarcane acreage. Partial government subsidy schemes support kieserite use in soil remediation for mining-affected zones, especially in northern sugarcane belts. In H2, planting and harvest cycles in southern Andes regions may sustain demand longer, implying a net 5–7% growth over H1. Price volatility should be moderate; increased volumes may prompt a slight upward adjustment—approx 3%, particularly if port throughput constraints persist.
2.2 Colombia
Colombia imported nearly 19,000 tonnes of kieserite in 2023, from China and Germany, with China accounting for ~41% of volume. With expanding fruit exports and sugarcane production, preliminary Q2 2025 import data indicate flat to modest growth (~2%) in Colombian demand. Given political uncertainty and road transport bottlenecks, H2 demand may remain flat or increase marginally (~2–3%). Price sensitivity is low; demand-volume stability suggests limited price change (<2%), unless logistical turbulence causes supply delays.
2.3 Costa Rica
Costa Rica’s import usage remains stable, primarily driven by fruit (notably mango) growers who apply kieserite to amend magnesium-deficient soils in smallholdings. Typical import volumes per grower are small—1–2 containers per season—and overall national volumes are modest. H2 2025 demand is expected to remain flat, or increase slightly (~1–2%), aligned with mango export peaks in Q4. Given limited volume and high fragmentation, any price variation is negligible.
2.4 Chile
Chile’s mature agricultural sector—including avocado and sugarcane regeneration programs—reported a 5.4% import increase in Q1 2025. Regenerative protocols emphasise sulphur-enriched fertilisers to sustain soil health in avocado orchards in the Maule and Coquimbo regions. H2 demand is projected to rise by ~6–8%, reflecting ongoing programs and greenhouse restocking. Price sensitivity is moderate: increased bulk orders may trigger a 3–4% rise, especially if shipment scheduling tightens before harvest.
2.5 Brazil
Brazil’s Q4 planting cycle historically prompts a 25–30% quarterly increase in kieserite demand. With planting acreage growing 8% in 2025, demand is projected to increase similarly. Record fertiliser imports of 44.3 million tonnes in 2024, up 8.3% YoY and deliveries near 45.6 million tonnes support this trend. Consequently, H2 demand may grow 7–10%, with associated price pressures of 5–8%, particularly around late planting windows in October–December.
3. Europe
3.1 Poland
Poland’s organic farming sector has increased kieserite usage by approximately 10% over two years, especially in certified blends for hemp, hops, and organic vegetables. Imports for H1 2025 continued growth, and H2 demand is expected to rise by 5–7% as EU organic acreage grows. Because contract terms are fixed sequentially, price effects are likely to be modest and gradual, anticipated at a 2–3% upward movement, mainly due to input and compliance cost pressure.
3.2 Netherlands
The Netherlands expanded imports by 4.3% YoY in early 2025, driven by greenhouse floriculture and personal-care manufacturing (kieserite is used in bath salts and mineral supplements). Anticipated restocking before the autumn flowering season could lift demand by 5–6% in H2. Because much is agreed via long-term supply contracts, price influence is limited, with a possible 2–3% incremental price effect based on volume-restocking schedules.
3.3 France
France imported roughly 22% of its kieserite needs from China in early 2025. The nutrient is used in certified fertiliser blends for certified vegetables, cereals, and sugar beet production. H2 2025 demand may flatten or slightly increase (~2–4%), depending on EU subsidy cycles. Price movement is influenced by upcoming CBAM compliance: expected CBAM cost add-ons of 8–12 USD/tonne equivalent will gradually translate into higher landed costs, prompting some buyers to renegotiate contracts or explore alternative suppliers. This regulatory shift may induce 3–5% upward pressure on price despite stable volumes.
3.4 Spain
Spanish imports remained stable in H1, with kieserite used in citrus and olive fertilisers. Farmers source kieserite in certified blends to meet EU traceability and purity mandates. In H2, olive harvest demand is seasonal; import volumes may increase by ~4–5%. Price volatility could be slightly higher (€5–7/MT equivalent) due to CBAM and logistics shifts, possibly translating into a 3–4% domestic price increase.
4. Africa
In Africa, kieserite continues to serve an important role in select national agricultural systems, with Egypt, Kenya, and South Africa being among the more active importers. These countries utilise kieserite primarily in horticultural applications such as floriculture and vegetable production, as well as in citrus orchards where magnesium deficiency is a known agronomic issue. For the second half of 2025, demand in Kenya is projected to increase by approximately 3–5%, supported by the expansion of greenhouse flower cultivation and certified vegetable export programs. In contrast, South Africa's demand is expected to remain largely stable or show a marginal decline of up to 1%, due in part to domestic economic factors and a partial substitution toward localised NPK fertiliser formulations. Nigeria, while still at an early stage in its kieserite adoption, has shown potential in recent trade registers, though current volumes remain limited. Overall, the African continent is forecast to experience a modest increase in kieserite demand in H2 2025—within the range of 1–3%—with limited impact on pricing due to relatively moderate total import volumes and continued influence of freight costs on purchasing behaviour.
5. North America
5.1 Canada
Eastern Canada’s cereal, vegetable and berry sectors saw Chinese kieserite import growth of approximately 5% YoY in H1 2025, used to address magnesium-deficient soils, notably in berry farms in Nova Scotia and vegetable rotations in Ontario. H2 demand is expected to increase by 4–6%, aligned with spring planting schedules. Pricing is moderately sensitive due to contract stability; expected price rise is 2–3%, reflecting shipping cost variation and seasonal inventory positioning.
5.2 Mexico
Mexico’s Q1 2025 imports increased 8%, driven primarily by fruit growers (mango, avocado, berries) who apply kieserite to address magnesium deficiency in the spring season. Given ongoing crop cycles and agricultural extension programs, H2 demand may rise further by 6–8%. Price influence is moderate: higher volumes and time-sensitive shipping could drive a 3–4% price uptick, though long-term contracts may limit variation.
Demand Forecast for 2026
Looking ahead to 2026, demand is expected to grow 3–6% year-on-year across most key markets:
Markets exhibiting above-average growth include Brazil, Peru, and Chile, due to expanding acreage and regenerative practices. Stable/modest growth is expected in Malaysia, Mexico, and Poland. Minimal change or flattening demand is likely in Colombia and Costa Rica, given confined small-holder usage.
Overall interplay of volume growth, seasonality, and incremental regulatory cost burdens (e.g. CBAM) suggests global kieserite pricing may experience moderate upward adjustment corresponding to annual demand growth rates, typically translating into 2–4% price increases in most markets.
Conclusion
In summary, most major importing markets for Chinese kieserite—including Southeast Asia, South America, Europe, and North America—are projected to experience modest to moderate demand increases (ranging from 2–10%) in H2 2025, driven by planting cycles, subsidies, and crop nutrition demands. Price fluctuations are expected to be contained, generally rising 2–5% where volume growth is solid and logistical or regulatory constraints are mild. In 2026, 3–6% demand growth across regions will likely support gradual pricing resilience, particularly as compliance costs such as CBAM begin to impact landed import parity.
China’s export relevance remains central, as its logistical efficiency and scale position it to reliably meet growing global kieserite demand, while maintaining its position as a pricing anchor in the international fertiliser landscape.
If you have any questions, please fill in the relevant information. We are very willing to provide more information and a full range of services for both you and your company.